Grinding with superabrasives is a procedure in which the cutting part of the abrasives consists of a large number of non-uniformly distributed cutting edges. These cutting edges are formed using superabrasive grit. Superabrasiveparticles are bonded into the abrasive ring of the grinding tool together with certain fillers using phenol – formaldehyde or polyimide resin. The abrasive ring on the grinding tool core, which provides appropriate strength and rigidity, reduces vibrations and the heat.
Basic grinding factors
- Workpiece ; material, shape, hardness
- Type of drinding
- Grinding tool; appropriate shape and core, appropriately selected components of the abrasive ring
- Dressing of the grinding tool
- Cooling and lubrication
- Type and condition of the grinding machine
The efficiency and cost-efficiency of grinding with superabrasive grit are affeced by all the above factors.
This catalogue focuses primarily on the correct selection of grinding tools, as well as on the interactions and our recommendations regarding other factors.
Superabrasive grit
Various types of CBN and diamond grits are used as superabrasives in grinding tools.
Some samples are shown on the pictures below
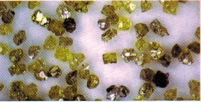 |
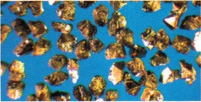 |
Synthetic diamond |
Cubic boron nitride |
In comparison with standard abrasives (aluminum oxide, silicon carbide), CBN and diamond grits are distinguished by greater hardness (H), wear resistance and thermal conductivity.

As the hardest abrasive material, diamond grits are used in the production of grinding tools for grinding and finishing tungsten carbides, combinations of tungsten carbides with steel and tools made of Polycrystalline diamond, ceramics, etc.
CBN grits are the second hardest abrasive material, but have a greater thermal stability than diamond grits.
They are suitable for working high-speed steels, chromium steels, cementing steels, steels for hot and cold treatment and steels for ball bearings. The majority of superabrasives in the production of resin bonded grinding tools are coated with a metal coating which provides them better retention in bond matrix and teat transfer from the abrasive grit to its surroundings.
Diamond and Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) are resistant to wear and are the hardest abrasives available today, suitable for materials that cannot be ground with conventional abrasive wheels. Both Diamond and CBN abrasives have similar structures. Diamond consists of pure carbon; CBN is composed of boron and nitrogen. Despite their physical relationship, their behavior differs in application.
Type of materials can be machined by Diamond and CBN grinding wheels
| Diamond Grinding Wheels |
CBN Grinding Wheels |
- Tungsten Carbide
- Glass
- Precious and Semi-Precious Gems
- Glass Reinforced Plastics (GRP)
- Ferrite
- Graphite, Electrocarbon
- Granite, Marble, Concrete
- Ceramics & Refractories
|
- High Speed Steel (HSS)
- Tool Steels
- Alloyed Steels
- Stellite
- Case Hardened Steels
- Heat Treated Steels
- Stainless Steels
- Bearing Steels
|
Application of Diamond and CBN grinding tools
| Type |
Bond |
Application |
|
Vitrified |
Resin |
Metal |
|
Synthetic Diamond |
SD4G |
+ |
|
|
Grinding of glass, crystal, ceramics, magnetic materials. |
SD6C |
+ |
|
+ |
Cutting of carbides, ceramics, glass, incl. quartz and optical glass. |
SDV15 |
+
+
+
+ |
|
+
+
+
+ |
Highly efficient grinding of carbides and advanced ceramics.
Honing. |
SDV20 |
SDV30 |
SDV50 |
SD4R |
|
+
+ |
|
Carbide cutter grinding. |
SD6R |
SHL |
+ |
+ |
+ |
Finish grinding and honing, lapping, polishing of carbides, ceramics. |
CBN (Cubic Boron Nitride) |
AVB40 |
+ |
|
|
Grinding of treated steels : hardened, nitride, cemented. |
AVB50 |
+ |
|
|
Highly efficient(incl. high-speed and creep-feed) grinding of treated steels, chilled cast iron and wear-resistant coatings. |
AVB60 |
+ |
|
|
Highly efficient grinding in extra heavy conditions. |
ARB40 |
|
+ |
|
HSS (high-speed steel) cutter grinding. |
ARB50 |
|
+ |
|
Highly efficient, incl. creep-feed, cutter grinding. Chip flute grinding. |
ASL |
+ |
+ |
|
Finishing, Superfinishing, lapping, polishing. |
4
The grit size determines the stock removal rate and the surface finish of the workpiece. Coarse grit gives high stock removal rates, fine grit improves finish with reduced stock removal rates. The standard grit sizes for Diamond and CBN are shown in this table, together with FEPA standard and other grit size designations. The FEPA standard is for both Diamond and CBN wheels. The code letter ‘D’ represents Diamond and CBN is represented by the prefix ‘B’
| Internation Standardization of Grit Sizes for Diamond and Cubic Boron Nitride |
Sieve grit designation |
Micron grit designations |
Diamond
FEPA-Standard
designation |
CBN
FEPA-Standard
designation |
Diamond + CBN
US Standard
ASTM-E-11-70 |
Nominal
Mesh
to ISO R565-1972
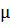 m m |
Diamond
FEPA Grit
designation |
CBN
FEPA Grit
designation |
ISO Range
R 565-1972
Mesh Widths
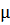 m m |
D 1181 |
B 1181 |
16/ 18 |
1180/ 1000 |
D 35 |
B 35 |
38-32 |
D 1001 |
B 1001 |
18/ 20 |
1000/ 850 |
D 30 |
B 30 |
38-25 |
D 851 |
B 851 |
20/ 25 |
850/ 710 |
D 25 |
B 25 |
32-25 |
D 711 |
B 711 |
25/ 30 |
710/ 600 |
D 20 |
B 20 |
25-20 |
D 601 |
B 601 |
30/ 35 |
600/ 500 |
D 16 |
B 16 |
25-15 |
D 501 |
B 501 |
35/ 40 |
500/ 425 |
D 15 |
B 15 |
20-10 |
D 426 |
B 426 |
40/ 45 |
425/ 355 |
D 10 |
B 10 |
12-6 |
D 356 |
B 356 |
45/ 50 |
355/ 300 |
D 7 |
B 7 |
10-5 |
D 301 |
B 301 |
50/ 60 |
300/ 250 |
D 3 |
B 3 |
5-2 |
D 251 |
B 251 |
60/ 70 |
250/ 212 |
D 1 |
B 1 |
2-1 |
D 213 |
B 213 |
70/ 80 |
212/ 180 |

Grits recommended WORLD DIAMOND TOOLS
Equivalent FEPA Standard is in
Preparation for grit size <D46
FEPA = Fe’ de ’ration Europe’ enne des
Fabricants deProduitsAbrasifs. |
D 181 |
B 181 |
80/ 100 |
180/ 150 |
D 151 |
B 151 |
100/ 120 |
150/ 125 |
D 126 |
B 126 |
120/ 140 |
125/ 106 |
D 107 |
B 107 |
140/ 170 |
106/ 90 |
D 91 |
B 91 |
170/ 200 |
90/ 75 |
D 76 |
B 76 |
200/ 230 |
75/ 63 |
D 64 |
B 64 |
230/ 270 |
63/ 53 |
D 54 |
B 54 |
270/ 325 |
53/ 45 |
D 46 |
B 46 |
325/ 400 |
45/ 38 |
Selection of superabrasive grit size
The size of abrasive grits determines the effect of grinding. The most cost-effective choice is the coarsest granulation that still achieves the required surface finish. If a greater amount of materials needs to be removed during grinding, a combination of coarse grinding and finish grinding is the most cost-effective.
In the table, grit size according to the FEPA, US ASTM and ISO-R565-1972 standard are stated for comparison, To simplify, one can view the sizes according to the FEPA standard as approximately corresponding to mean grit size in microns (D126 is approx. 0.126 mm),
|
FEPA |
ASTM-E-11-70 |
ISO-R565-1972 |
Coarse grinding |
213
181
151
126 |
70/80
80/100
100/120
120/140 |
212/180
180/150
150/125
125/106 |
Medium fine grinding |
107
91
76 |
140/170
170/200
200/230 |
106/90
90/75
75/63 |
Fine grinding |
64
54
46 |
230/270
270/325
325/400 |
63/53
53/45
45/38 |
POLISHING
Micron size |
World Diamond
Designation |
D35 |
D25 |
D15 |
D7 |
Size - m m |
38-32 |
32-25 |
20-10 |
10-5 |
All quality characteristics of the grinding tool are determined by the workpiece type and material, grinding method and the grinding machine, while the abrasive grit size is selected on the basis of the required grinding depth and surface quality.
GRIT SIZE ACCORDING to FEPA |
Surface finish
R (micron) |
Surface quality
N |
GRINDING METHOD |
Diamond |
CBN |
|
B181 |
1.12 |
N7-N6 |
Very coarse grinding |
|
B151 |
0.75 |
N6 |
|
B126 |
0.66 |
N6 |
D181 |
B107 |
0.53 |
N6-N5 |
D151 |
B91 |
0.50 |
N6-N5 |
D126 |
B76 |
0.45 |
N6-N5 |
D107 |
B64 |
0.40 |
N5 |
D91 |
B54 |
0.33 |
N5-N4 |
Medium fine grinding |
D76 |
B46 |
0.25 |
N5-N4 |
D64 |
B35 |
0.18 |
N4 |
D54 |
B30 |
0.16 |
N4-N3 |
D46 |
B25 |
0.15 |
N4-N3 |
Sizes-Micron |
|
|
N3-N2 |
Polishing |
The table applies to the grinding of tungsten carbides K20 and HSS-64 HRc.
As shown in the table, CBN grit size for grinding must be 2-3 grades smaller in order to achieve the same surface quality as with diamond abrasives. The achieved surface quality also largely depends on the grinding procedure, specific material removal rate, workpiece material and cooling.
Hardness
Hardness is a characteristic of vitrified wheels
Grade groups |
Soft |
Medium |
Hard |
W.D.T Standard |
S1 |
S2 |
M1 |
M2 |
M3 |
H1 |
H2 |
H3 |
H4 |
International Standard |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
Bonds
Diamond and CBN grinding wheels are manufactured to a high standard in various bond types – Vitrified, Resin, Metal and Electroplated. The bond type is selected according to the grinding requirements.
1. Vitrified bond
Vitrified grinding wheels give good stock removal and are more suited to high operating speeds (40-60m/sec) using pressure coolant. Diamond vitrified wheels are excellent for grinding Polycrystalline diamond tools. CBN vitrified products are excellent for grinding hard steels and irons. Vitrified wheels are manufactured in a limited range of sizes and shapes.
2. Resin bond
Resin bond grinding wheels give good stock removal rates and are free cutting. Resin bond wheels are commonly used for grinding tungsten carbide and combinations of carbide and steel. CBN resin wheels are excellent for grinding high speed steel alloys.
3. Metal bond
Metal bond wheels are more wear resistant than resin bonded types, harder in operation and ideal for use in an abrasive environment. They should always be used with coolant to avoid component damage.
4. Electroplated bond
Electroplated wheels have only a single layer of Diamond or CBN, are very free cutting and give high stock removal rates. Wheels made by this process do not maintain their performance over long grinding periods. The system does allow special profile wheels to be manufactured at relatively low cost.
Bond types used in wheel production
Type/Bond |
Vitrified |
Resin |
Metal |
Diamond |
VD 11D |
RWD12B, RD13B, RW14B, RD15B |
MG-01, MC-02 |
CBN |
VI 9B, VC 10B |
RWD12B, RD13B, RW14B, RD15B |
|
Bonds Application Guide
Bond types |
Application |
Vitrified |
VI 9B |
For internal grinding, profile grinding |
VC 10B |
For cylindrical, centreless, surface grinding |
VD 11D |
For grinding with synthetic diamond wheels only |
Resin |
RWD 12B |
Universal bond for wet/dry grinding in normal grinding conditions on CNC machines |
RD 13B |
For dry grinding, for cup wheels with rim width W> 5 mm |
RW 14B |
For wet grinding, for wheels with the narrow rim (w  5 mm), for grinding on CNC machines, for cut-off wheels 5 mm), for grinding on CNC machines, for cut-off wheels |
RD15B |
For dry grinding in heavy grinding conditions, for wheels with the narrow rim (w  5 mm) 5 mm) |
Metal |
MG-01 |
For grinding of glass and ceramics with synthetic diamond wheels |
MC-02 |
For cut-off synthetic diamond wheels |
Bond selection criteria |
Softer bonds better |
Harder bonds better |
Grinding width |
Wide |
Narrow |
Grit size |
Fine |
Coarse |
Concentration |
Lower |
Higher |
Workpiece hardness |
Harder |
Softer |
Applications |
Dry |
Wet |
Other criteria |
Better thermal conductivity |
Better grit retention |
Comparison of results |
Softer bonds |
Harder bonds |
Material removal capacity |
Great grinding action |
Smaller grinding action |
Relative material removal rate |
Freer grinding action |
Smaller grinding efficiencies |
Grinding pressure |
Smaller |
Great |
Grinding factor G |
Smaller |
Great |
Grinding wheel life |
Higher wear rate (shorter wheel life) |
Lower wear rate (longer wheel life) |
Contact surface temperature |
Lower |
Higher |
Concentration
This is the ratio of Diamond or CBN to the volume of the abrasive section of the wheel. The correct selection of concentration is very important as it affects the speed of cut, the surface and finish achieved, the durability of the wheel and its cost. Our staff are always available to offer advice on the requirement for your particular application.
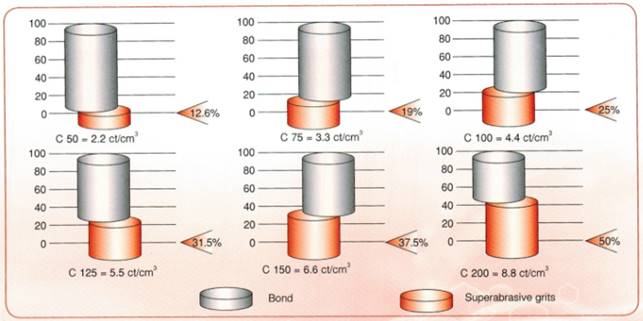
Correspondence Chart of Concentration in % and carat/cm3
Concentration of Diamond/CBN in a grinding wheel, % |
50 |
75 |
100 |
125 |
150 |
200 |
Content of Diamond/CBN in a grinding wheel, carat/cm3 |
2.2 |
3.3 |
4.4 |
5.5 |
6.6 |
7.7 |
The selection of the concentration depends on different factors and can be outlined, as followed :
Low concentration (50%) is used in the wheels with the microgrit size D35 and finer.
Medium concentration (75% : 100%) is used in most grinding operations, in wheels with the layer grit size from D126 to D64, also in cup wheels with the wide abrasive layer (7-20mm.)
High concentration (125-200%) is used in the following cases :
• in wheels with the grit size D151 and higher – to increase the quantity of the grains and, thus, to reduce working load on each grain ;
• in wheels with a small outer diameter (D<50 mm) - to increase the quantity of the grains in the grinding zone; in profile grinding wheels for better profile (form) maintenance; in cup wheels with the abrasive layer width 5 mm and less.
Superabrasive grit concentration
The concentration should be selected with respect to the grinding procedure.
Low concentrations are recommended for fine abrasive grits, large contact surfaces between the abrasive and workpiece and in manual grinding; high concentrations are more suitable for coarse grits, small contact surfaces and whenever large profile stability of the grinding tool is required.
This is expressed as the quantity of diamond cubic boron nitride grits in carats/cm3 of the abrasive ring (1 ct = 0.2 g). The diagrams show the volume percentage of superabrasive grit in the abrasive ring.
Core material
Choice of wheel core material is important as it can affect the wheel performance. Core materials can influence heat dissipation, vibration suppression and dynamic strength of the tool. Selection available – phenolic resins, which can be filled with aluminium or abrasive, or solid metals such as aluminium or steel.
Worst 
Best     
Alumina-Bakelite - Medium weight material used for rigid grinding wheel bases. It adequately dampens vibrations, removes heat and provides good mechanical strength. For example grinding wheel 11V9, 12V9 shapes.
Abrasive Ceramic Base - This material has the same mechanical properties as alumina – bakelite and is suitable primarily for less demanding applications and smaller, heat generated during grinding are dissipated quickly. They are used in the dry grinding applications in the Cabide Dies Industries. For example grinding wheel 1A1 shapes (up to D=200mm). It can also be used when full wear/use of the diamond ring is desired.
Duraluminium - A heavier material which should be used when more stable bases are needed. It provides good mechanical strength and also better heat removal than alumina – bakelite. They are best suited for the used in CNC grinding applications.
Steel Base - Steel bases are significantly heavier than the other four types of materials. They are used whenever good mechanical properties need to be ensured even with thin abrasives, for example cutting – off wheels (1A1R).
Bakelite Base - A lighter material with very good vibration dampening properties.
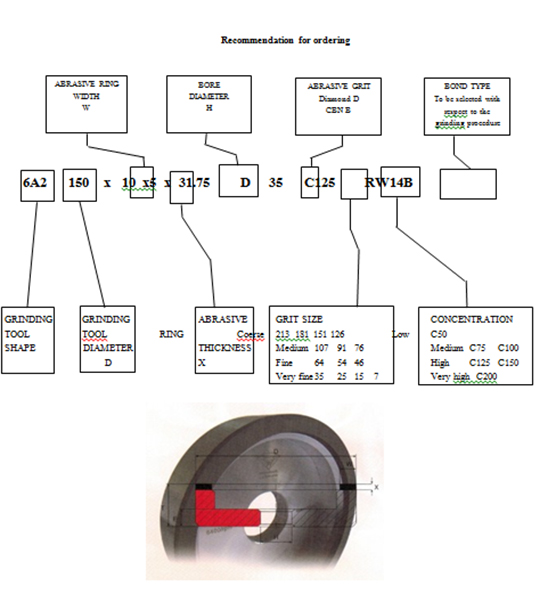
RECOMMENDATIONS AND TIPS FOR SELECTING
OPERATING PARAMETERS
Apart from a correct selection of grinding tool type and quality, it is important to observe recommendations on peripheral speeds, which are given is the table below (along with ipm) for optimum grinding with World Diamond Superabrsive.
Recommended peripheral speeds
|
Speeds VS(m/s) |
|
Diamond grinding tools |
CBN grinding tools |
GRINDING PROCEDURE |
Wet grinding |
Dry grinding |
Wet grinding |
Dry grinding |
Flat surface grinding |
20-30 |
15-20 |
22-35 |
15-22 |
Internal cylindrical grinding |
10-20 |
8-12 |
18-30 |
15-20 |
External cylindrical grinding |
20-30 |
- |
25-35 |
18-22 |
Tool sharpening |
18-28 |
15-22 |
20-30 |
18-25 |
CNC tool grinding |
18-22 |
- |
30-70 |
- |
Diagram for determining grinding tool rpm
 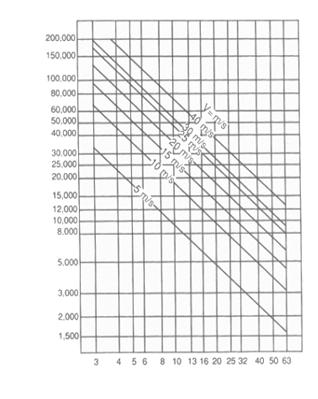 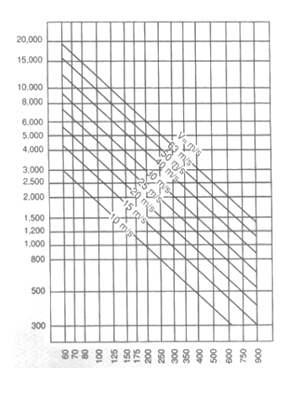
Grinding tool diameter (mm)
Table Wheel Peripheral Speed
Wheel
Dia.MM |
Spindle Revolutions Per Minute/Per Second Periperal Speed |
10 m/s |
15 m/s |
20 m/s |
25 m/s |
30 m/s |
35 m/s |
40 m/s |
45 m/s |
50 m/s |
60 m/s |
20 |
9550 |
14725 |
19100 |
23875 |
28650 |
33440 |
38215 |
42990 |
47770 |
57300 |
25 |
7460 |
11460 |
15280 |
19100 |
22920 |
26750 |
30570 |
34390 |
38215 |
45800 |
30 |
6365 |
9950 |
12730 |
15915 |
19100 |
22290 |
25475 |
28660 |
31845 |
38200 |
50 |
3820 |
5730 |
7640 |
9550 |
11460 |
13375 |
15285 |
17195 |
19105 |
22800 |
75 |
2545 |
3820 |
5095 |
6370 |
7640 |
8915 |
10190 |
11465 |
12735 |
16350 |
100 |
1910 |
2865 |
3820 |
4775 |
5730 |
6685 |
7640 |
8600 |
9550 |
11450 |
125 |
1530 |
2290 |
3055 |
3820 |
4580 |
5350 |
6115 |
6880 |
7640 |
9180 |
150 |
1275 |
1910 |
2545 |
3180 |
3820 |
4460 |
5095 |
5730 |
6370 |
7600 |
175 |
1090 |
1640 |
2185 |
2730 |
3280 |
3820 |
4367 |
4910 |
5460 |
6500 |
200 |
955 |
1435 |
1910 |
2390 |
2865 |
3340 |
3820 |
4300 |
4780 |
5700 |
250 |
765 |
1145 |
1530 |
1910 |
2290 |
2675 |
3055 |
3440 |
3820 |
4590 |
300 |
635 |
905 |
1275 |
1590 |
1910 |
2230 |
2545 |
2865 |
3185 |
3800 |
350 |
545 |
820 |
1090 |
1365 |
1640 |
1910 |
2180 |
2455 |
2730 |
3260 |
400 |
480 |
715 |
955 |
1194 |
1435 |
1670 |
1910 |
2150 |
2390 |
2880 |
450 |
425 |
635 |
850 |
1060 |
1275 |
1485 |
1700 |
1910 |
2120 |
2550 |
 Dressing of grinding tools and opening of the structure Dressing of grinding tools and opening of the structure
If the grinding parameters are not optimal, the abrasive ring wears unevenly.
Vitrified bonded(SiC) grinding tools G-K are used for dressing. Their grit size must be
one grade coarser than that of the superabrasive grits, which are dressed. Both grinding
tools here revolve in the same direction, whereby the peripheral speed of the SiC grinding
tool is 15-25 m/s, and that of the superabrasive grinding tool is lower by half. Grinding
tools with abrasive rings on the face can also be dressed by rubbing them against SiC
160-180 abrasive grits, which are applied onto a flat metal or glass surface.
This reopens the surface of a dulled grinding tool, even though the grinding tools are already self-sharpening when correctly used. The structure of dulled grinding tools can also be opened using a grinding stone, which is enclosed with the grinding tool. A wet grinding stone is pressed against the rotating grinding tool by hand. Resin bonded CBN grinding tools for flat surface grinding of hardened steels are sometimes also dressed by grinding into soft steels at a peripheral speed of approx.15 m/s
Shape Description
FEPA – IDENTIFICATION CODE FOR DIAMOND OR CBN WHEEL SHAPES
With the exception of “SPECIALS” wheels for tool and cutter grinding, Please reference to the Woodworking and Plastics industries catalogue. World Diamond Superabrasive wheels are produced to FEPA Standard Shapes and Sizes.
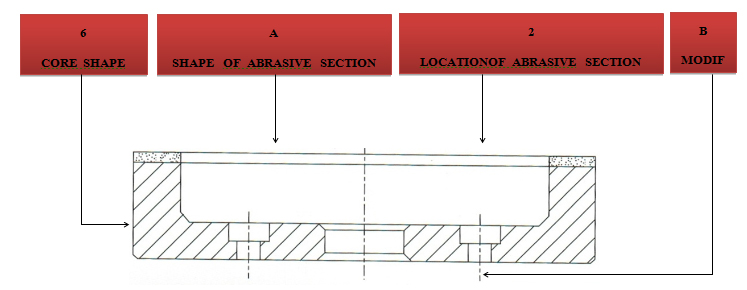
CORE SHAPESHAPE OF ABRASIVE SECTION
1
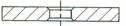 |
9
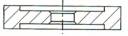 |
|
A
 |
D
 |
FF
 |
L
 |
Q
 |
2
 |
11
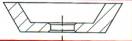 |
|
AH
 |
DD
 |
G
 |
LL
 |
S
 |
3
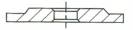 |
12
 |
|
B
 |
E
 |
H
 |
M
 |
U
 |
4
 |
14
 |
|
C
 |
EE
 |
J
 |
P
 |
V
 |
6
 |
15
 |
|
CH
 |
F
 |
K
 |
Q
 |
Y
 |
LOCATION OF ABRASIVE SECTION
1-Periphery
 |
3-Both Sides
 |
7-Part of Side
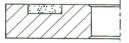 |
4-Inside Bevel or Arc
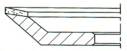 |
8-Throughout
 |
2- Side
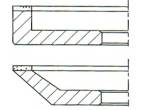 |
5-Outside Bevel or Arc
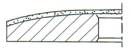 |
9-Corner
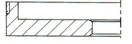 |
6-Part of Periphery
 |
10-Annular
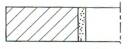 |
MODIFICATION
B-Drill and Counterbore
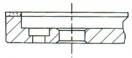 |
T-Threaded Hole
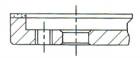 |
SS-Segmented and Slotted
 |
C-Drill and Countersunk
 |
P-Relieved One Side
 |
Q-Inserted
 |
H-Plain Hole
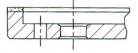 |
R-Relieved Two Side
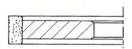 |
V-Inverted
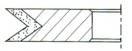 |
M-Holes Plain and Threaded
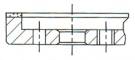 |
S-Segmented Abrasive Section
 |
Y-Inserted and Inverted
 |

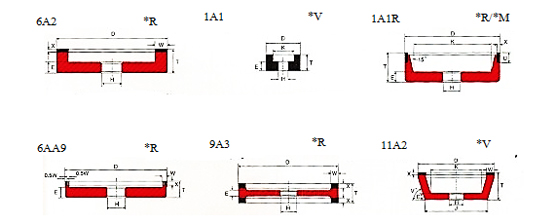
*V = Vitrified Bond Wheels *R = Resin Bond Wheels *M = Metal Bond Wheels
*VD = Vitrified Diamond Wheels *VB = Vitrified CBN Wheels
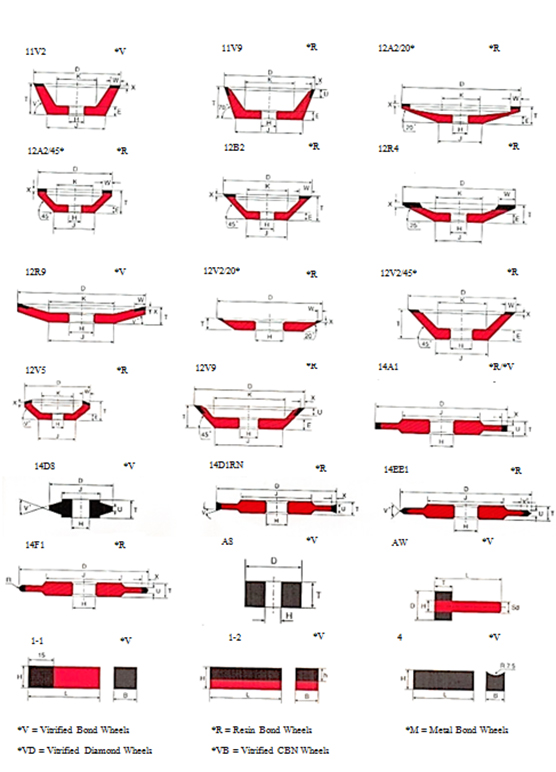
Shapes of grinding tools
These are designated according to EN 13236 and FEPA standards. Selection of the most rigid types is recommended, as massive cores are less sensitive to impact and prevent vibrations. Also, cup shapes are better for face grinding than wheel shapes.
The following manufacturers/users are responsible for safety during grinding:
Grinding tool manufacturer
The grinding tool manufacturer must manufacture a safe tool, which is achieved through a correct selection of raw materials, a correct technological manufacturing procedure and the required product control:
- safety control (at increased peripheral speeds, cracks)
- quality control (dimensions, hardness, runout and balance)
Control methods are prescribed by the ISO 9001 : 2000 EN13236 and FEPA international standards, as well as World Diamond Superabrasive’s internal standards.
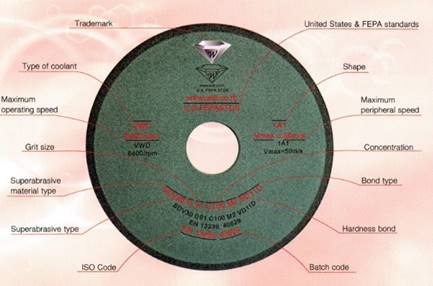
The following must be marked on grinding tools by the manufacturer:
- Logo (Trade mark)
- Product dimensions
- Quality (type and size of abrasive grit, bond quality and concentration)
 Max. peripheral speed Max. peripheral speed- Safety warning regarding tool use:
Most frequent markings on grinding tools:
Grinding machine manufacture
The grinding machine manufacturer must ensure a stable machine installation and strength of the protective housings.
The strokes and displacements must be set so that the required product accuracy can be achieved. Instructions for correct and safe use of the macine must also be prepared. |
